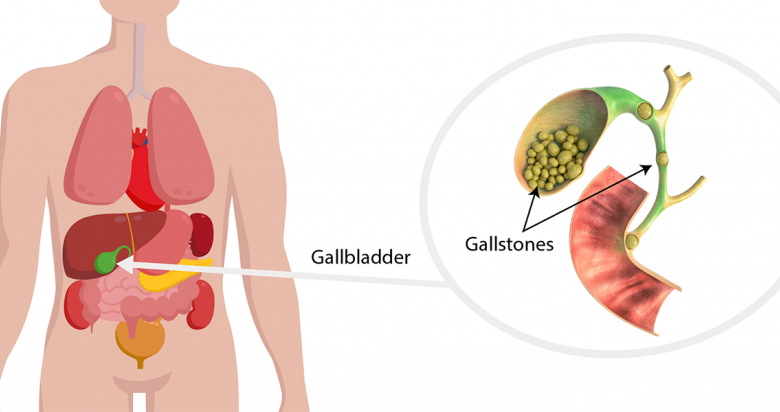
Gallstones, otherwise known as bile duct stones, are hardened digestive fluids that can buildup in the gallbladder. The presence of gallstones may not exhibit any symptoms at times, but signs occur when it is unable to travel through and becomes stuck in the bile duct. This article shares further information you need to know about this condition, the factors that increase an individual’s risk of developing it, and gallstones removal cost in Singapore.
Are you at high risk of developing gallstones? Here are six “F” factors that can determine your gallbladder’s health risk:
- Fair-skinned — Gallstones, particularly cholesterol gallstones, are common among fair-skinned or Caucasians. In addition, the condition is also highly observed among Native Americans, specifically those from the tribes of Navajo and Pima.
- Fat — Obesity causes over secretion of cholesterol from the excess fats that overwhelm the bile. Individuals that are obese have an increased risk of developing cholecystitis which can cause obstruction in the bile duct and also cholelithiasis.
- Female — Cholecystitis is found to affect females more than males, due to the high tendency of fat accumulation in women’s bodies.
- Fertility — This factor also affects women in general, especially in women who have given birth to more than one offspring. The common cause that triggers the development of gallstones in multiparous women is their inability to empty out the gallbladder completely, leaving concentrated amounts of bile in the gallbladder to harden and become stones. These stones can cause obstruction and result in cholecystitis. There is also a major risk for women who are receiving estrogen treatment for postmenopausal conditions.
- Flatulence — The smooth flow of bile becomes disrupted when the gallbladder is unable to work properly. This leads to the body’s inability and failure to digest fats properly, which can develop fatty food intolerance and flatulence as cholecystitis occurs.
- Forty — It is usual for our bodies to grow weak as we age. For people who are past the age of 40, the risk of developing gallstones increases.
Gallbladder: What is it?
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ that measures about 4 inches and is located at the upper-right side of the abdomen beneath the liver. This organ may be small, but its function is very crucial to digestion: it stores bile, a substance that breaks down fat from the food that we digest and carries waste to be processed and released from the body. When the liver secretes substances that overwhelm the bile’s ability to process, the excess secretions can harden and become gallstones.
Gallstones: What are the signs and symptoms?
As mentioned previously, gallstones can exist silently in the gallbladder. You will only know about their existence if you suddenly feel these symptoms:
- Chills
- Chronic diarrhea
- Fast heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Itching of skin
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Pain
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
Other symptoms that may be a possible symptom of gallstones:
- Jaundice or yellowing of skin and eyes
- Stool that is light-colored
- Urine that is dark-colored
Gallstones may have some signs and symptoms that are also common to other medical conditions, such as appendicitis, other gallbladder problems, and pancreatitis. The only way to accurately diagnose this condition is to have yourself checked by a doctor that specializes in the treatment of the digestive tract.
Gallstones: What are the causes?
A bile chemical imbalance that occurs in the gallbladder is what medical experts believe to be the main cause of gallstones. As to what triggers this imbalance remains a mystery, but it may be due to the following possibilities:
- Excess bilirubin in the bile
- Excess cholesterol in the bile
- Inability of bile to drain fully from the gallbladder
Excess bilirubin in the bile or Pigment Gallstones. Breaking down of the red blood cells results in the production of a chemical called bilirubin. As soon as it is produced, bilirubin travels through the liver and is carried out of the body as waste. There are certain medical conditions that affect the liver and blood that may cause the body, specifically the liver, to overproduce bilirubin. When this happens, the bile may not be able to process the surplus of bilirubin. As a result, the remaining bilirubin hardens and becomes pigment gallstones. These hard gallstones are black or dark brown in color.
Excess cholesterol in the bile or Cholesterol Gallstones. Aside from bilirubin, the bile is also responsible for breaking down cholesterol. Too much cholesterol than the bile can dissolve may cause it to harden and become yellow gallstones.
Inability of bile to drain fully from the gallbladder. Proper function of the gallbladder relies heavily on its ability to release bile completely. Being unable to do so can make the remaining bile extremely concentrated, which ends up in forming gallstones.
Gallstones removal in Singapore: What are the options?
There are several options available for gallstones removal in Singapore. These are:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP)
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Open cholecystectomy
- Medication
The table below shows how each procedure or treatment is carried out.
| Gallstones removal procedure or treatment | How the procedure or treatment is done |
| Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP) |
|
| Laparoscopic cholecystectomy |
|
| Open cholecystectomy |
|
| Medication |
|
Gallstones removal cost in Singapore based on MOH’s website are as follows:
| Procedure | Public Hospitals (Subsidised) | Public Hospitals (Unsubsidised) | Private Clinics/Hospitals |
| Gallbladder removal (Simple) | $3,000 – $4,000 | n/a* | $17,500 – $21,500 |
| Gallbladder removal (Simple) with bile duct inspection | $3,000 – $4,000 | n/a* | $8,000 – $13,000* |
| Open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Emergency/complicated) | $2,500 – $3,000 | $7,500 – $10,000 | $20,000 – $28,000 |
*Based on doctor’s operation fees. Total bill including tests, ward charges, and medication, is unavailable due to the low count of the procedure
Gallstones: Can they be prevented?
If you find yourself seeing a couple of red flags in the six “Fs” list in the beginning of this article, then you may want to consider making changes to your lifestyle to lessen your chances of developing gallstones. Here are some tips you can do:
- Eat foods packed with fiber – Fruits, whole grains, and vegetables are the best source of fibers. Include generous servings of these in your daily meals.
- Keep a healthy weight – Obesity is one of the factors that cause gallstones. Work up a sweat and keep your body’s weight at a healthy level by consuming just the right amount of calories it needs each day. Stay away from fatty foods that can cause cholesterol levels in the body to spurt.
- Lose weight gradually – If you are overweight or obese and would like to lose weight, do it at a slow pace. Target losing 2 pounds at most in one week so as not to increase your risk of developing gallstones.
To know more about gallstones removal, visit Gastrohealth.
Gastrohealth Clinic – Dr Bhavesh Doshi | Gastroenterologist | Colonoscopy Singapore
6A Napier Rd, #03-370 Gleneagles Hospital Annexe Block, Singapore 258500
+65 6355 5773
https://gastrohealth.com.sg/
Hi, I am an Author who believes in making the life of their readers interesting with his writing. Writing was always my first interest. Ever since I was a teenager, I was already into writing poems and stories. Today, I have gained a great experience in my work. Check out my work and share your views.