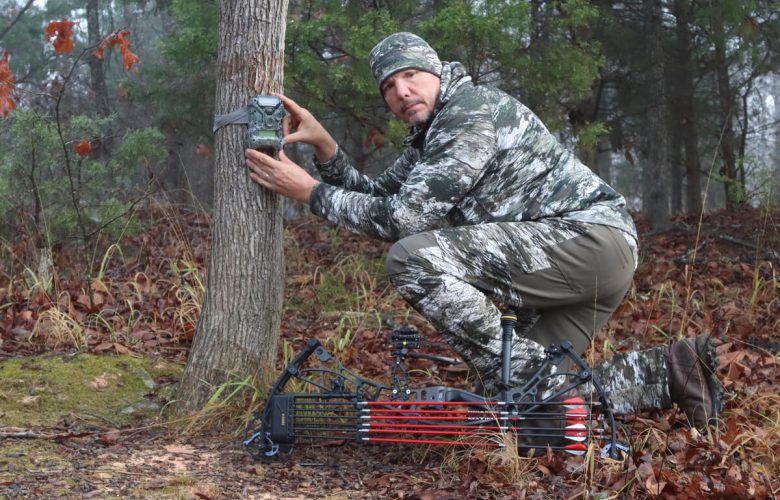
The wonderment of technology is experienced in various walks of life, and regarding photography, trail cameras have been one of its premier inventions. Originally designed for tracking game in the wilderness, trail cameras were a technological leap in the field of wildlife photography and research. Hunters utilized these cameras to scout hunting trails, hence the name trail cameras. Their usage quickly expanded beyond the hunting community to become invaluable tools for wildlife researchers, security personnel, farmers, and adventure enthusiasts.
Over the years, trail camera technology has advanced, making these devices more efficient, versatile and popular. They capture images triggered by movement and even in complete darkness, providing information about the wildlife that roam our forests. Continued advancements have led to high-resolution imagery, increasing accuracy and convenience for researchers and users alike.
Table of Contents
Early Trail Camera Technology
In their early stages, trail cameras were far from the efficient marvels that we see today. The primitive versions were often bulky and operated on chemical film that needed manual development after being exposed. Every instance of motion would trigger the shutter to snap a photograph. The film had a certain capacity and once all frames were exposed, it had to be manually replaced. This method of capturing images, while effective during its time, came with its fair share of limitations, including limited capacity, necessary regular maintenance and potential for human error during film development.
Modern trail cameras are more compact and come equipped with a plethora of advanced features that take their capabilities to greater heights. The older versions were devoid of the latest technology like high resolution imaging, night vision, motion sensors, trail camera management software, and wireless technology, which today’s cameras boast of. Operational efficiency, too, has seen a significant surge with modern trail cameras being more user-friendly and offering remote accessibility, thereby eradicating the need for constant physical check-ins.
Progression of Trail Camera Technology
The progression in trail camera technology is evident with the shift from chemical film to digital technology. Prior, when this process was manual, problems arose such as the films becoming exposed, fewer shots, and the need for frequent checking. With digital technology, more images can be stored and instantly viewed without the need for development. An even more impressive innovation is the introduction of motion-activated sensors. These sensors, often infrared, lay dormant until a subject (often a roaming animal) triggers the camera to capture a shot. This allows for more efficient use of battery and storage space.
Another major stride in trail camera technology is the integration of infrared technology for nighttime monitoring. Earlier models of trail cameras struggled with low light conditions, making nighttime wildlife monitoring a challenge. However, modern trail cameras come equipped with infrared flash, allowing them to take clear pictures or record videos in complete darkness without alerting the wildlife. The shift from visible flash to infrared flash technologies has made trail cameras “invisible” to animals and thus more effective in capturing naturally occurring behaviors.
Recent Advancements in Trail Camera Technology
Recent times have seen unprecedented advancements in trail camera technology. The ability to capture high-resolution images and HD video recording has completely transformed the potential of these cameras. Today, they are capable of capturing images in stunning detail, providing valuable data for researchers, hunters, and outdoor enthusiasts. In addition to visible light photography, advancements in low glow and no glow infrared technology have opened new avenues for nighttime wildlife watching.
The implementation of wireless technology and Global Positioning System (GPS) has revolutionized the user experience. With this technology, wildlife can be tracked in real-time and data can be transmitted wirelessly to a remote server or a handheld device, eliminating the need to physically retrieve the camera. More recent models have even incorporated a time-lapse mode, providing an interesting perspective on wildlife patterns. The integration of SIM cards and mobile application usage has enabled faster data access, allowing users to monitor and adjust their trail cameras from anywhere in the world instantly.
Impact of Technological Advancements on User Experience
The rapid progression in trail camera technology has dramatically enhanced user experience. One of the most notable impacts is the improved capture of wildlife behavior and patterns. High-resolution imagery and nighttime recording technology have provided researchers a more detailed understanding of wildlife, leading to newer discoveries and revelations. The implementation of motion sensors and time-lapse modes have distinctly helped in tracking wildlife movements precisely, documenting their patterns, routines, and interactions like never before, leading to a broader and more varied research possibility.
On a user level, easier operation and the convenience brought about by digital and wireless technologies cannot be stressed enough. One no longer needs to trek difficult terrains regularly to check on their cameras. With remote access and immediate data availability, adjustments can easily be made from the comfort of your own home, or basically anywhere with internet access. This has made the use of trail cameras less strenuous and more efficient for hunters, researchers, and wildlife enthusiasts alike. The advantages of these advancements have been transformative, making trail cameras more accessible, more user-friendly, and ultimately, more effective.
Trail cameras have undeniably advanced at an impressive pace. With the continual progression in their features and capabilities, they are helping to deliver a seamless user experience whilst contributing significantly to wildlife research, security and numerous other applications.